Service Delivery Systems: The Strategic Framework for Operational Excellence
In an era where customer expectations continue to rise and market dynamics shift rapidly, organizations must rethink how they design, deliver, and optimize their service offerings. Service Delivery Systems represent a comprehensive approach to transforming how businesses create value, manage operations, and exceed customer expectations at every touchpoint.
Understanding Service Delivery Systems
A Service Delivery System is an integrated framework that orchestrates people, processes, technology, and resources to consistently deliver exceptional service experiences. Unlike traditional service models that focus on isolated transactions, modern service delivery systems create interconnected ecosystems designed for efficiency, scalability, and continuous improvement.
The global service delivery platform market, valued at $6.54 billion in 2024, is projected to reach $11.92 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 7.8%, demonstrating the increasing recognition of systematic service delivery as a competitive differentiator.
These systems encompass the entire service lifecycle, from initial customer inquiry through post-delivery support and ongoing relationship management. They integrate front-end customer interactions with back-end operational processes, creating seamless experiences that drive both customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
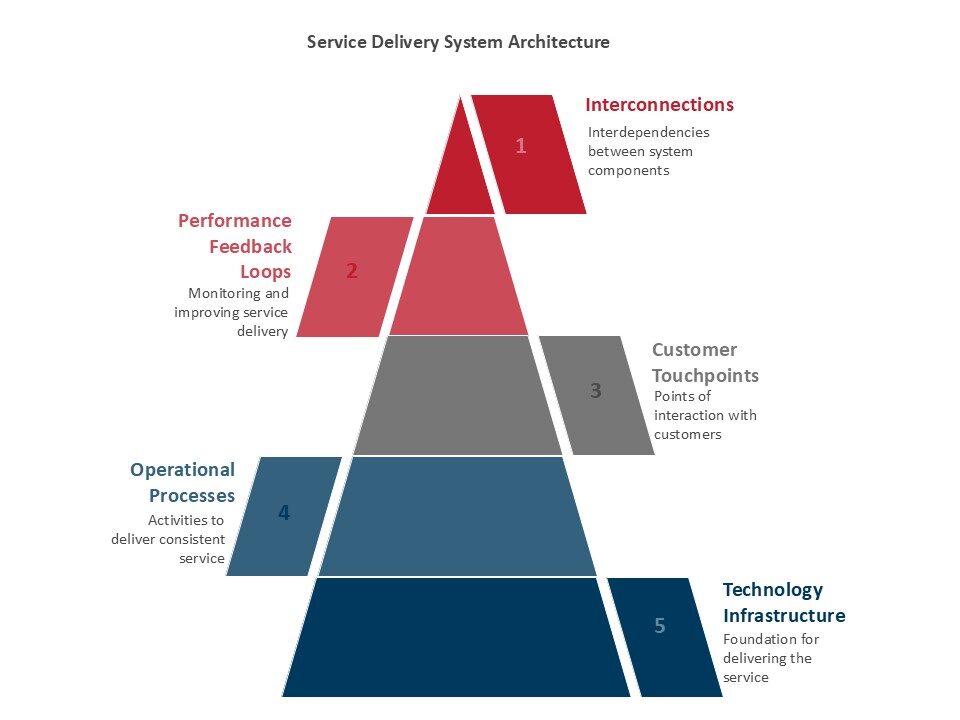
The Strategic Imperative for Systematic Service Delivery
Business Performance Impact
Organizations with well-designed service delivery systems demonstrate superior financial performance across multiple metrics. McKinsey research reveals that companies with strong design capabilities increase their revenues and shareholder returns at nearly twice the rate of their industry counterparts, with much of this advantage stemming from systematic approaches to service design and delivery.
The correlation between service excellence and business outcomes is particularly pronounced in today’s digital economy. Companies that excel at service delivery typically achieve higher customer lifetime values, reduced churn rates, and increased cross-selling opportunities.
Operational Efficiency Gains
Systematic service delivery eliminates redundancies, reduces errors, and optimizes resource allocation. By standardizing processes while maintaining flexibility for customization, organizations can achieve significant cost savings while improving service quality. These efficiencies become particularly important as businesses scale and complexity increases.
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Modern consumers expect consistent, personalized, and frictionless service experiences across all channels. Recent HubSpot research indicates that 47% of customer service representatives describe their service as “very personalized,” while 45% describe it as “somewhat personalized”, highlighting both the emphasis on customization and the opportunity for improvement through systematic approaches.
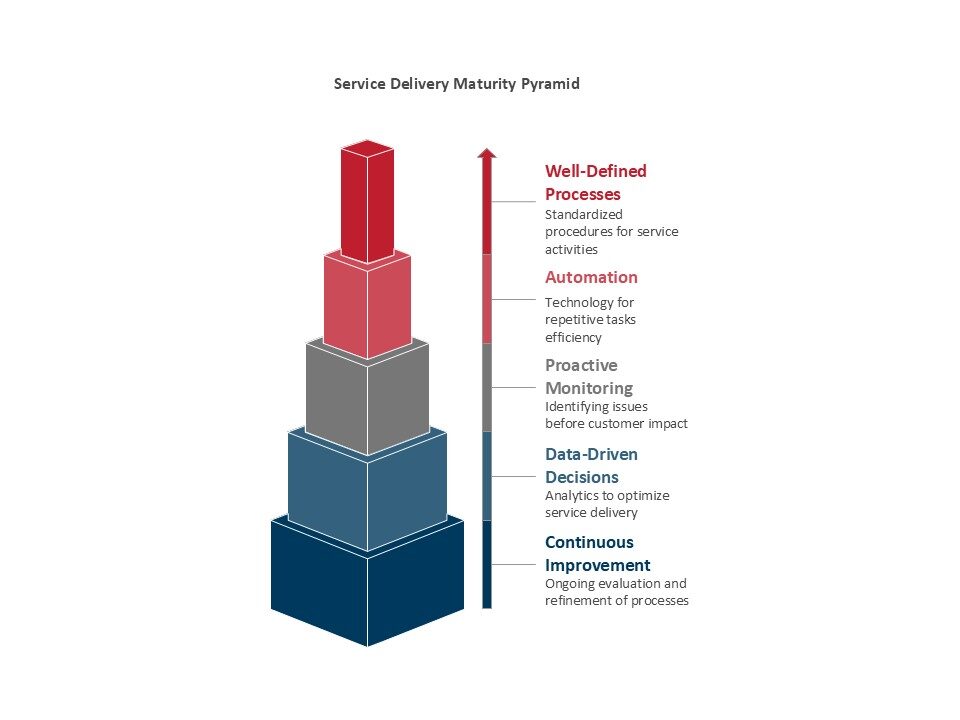
Core Components of Effective Service Delivery Systems
Service Design Architecture
The foundation of any effective service delivery system is thoughtful service design that considers the entire customer journey. This involves mapping all touchpoints, identifying moments of truth, and creating service blueprints that guide both customer-facing and behind-the-scenes activities.
Effective service design balances standardization with flexibility, ensuring consistent quality while allowing for customization based on specific customer needs or market segments. The architecture must also account for scalability, accommodating growth without compromising service quality.
Process Optimization and Standardization
Systematic service delivery requires clearly defined, documented, and optimized processes. These processes should be designed with both efficiency and effectiveness in mind, eliminating unnecessary steps while ensuring all critical activities are performed consistently.
Process standardization doesn’t mean rigidity. The best service delivery systems incorporate adaptive elements that allow for situational adjustments while maintaining overall consistency and quality standards.
Technology Integration and Automation
Modern service delivery systems leverage technology to enhance human capabilities rather than replace them entirely. This includes customer relationship management platforms, workflow automation tools, communication systems, and analytics platforms that provide real-time insights into system performance.
Current research shows that 31% of organizations are in the developing stage of AI implementation, where technology is changing workflows and increasing efficiency, indicating significant opportunities for businesses to enhance their service delivery through intelligent automation.
Performance Measurement and Continuous Improvement
Effective service delivery systems include robust measurement frameworks that track both operational metrics and customer outcomes. These systems provide the data necessary for continuous optimization and help identify emerging issues before they impact customer satisfaction.
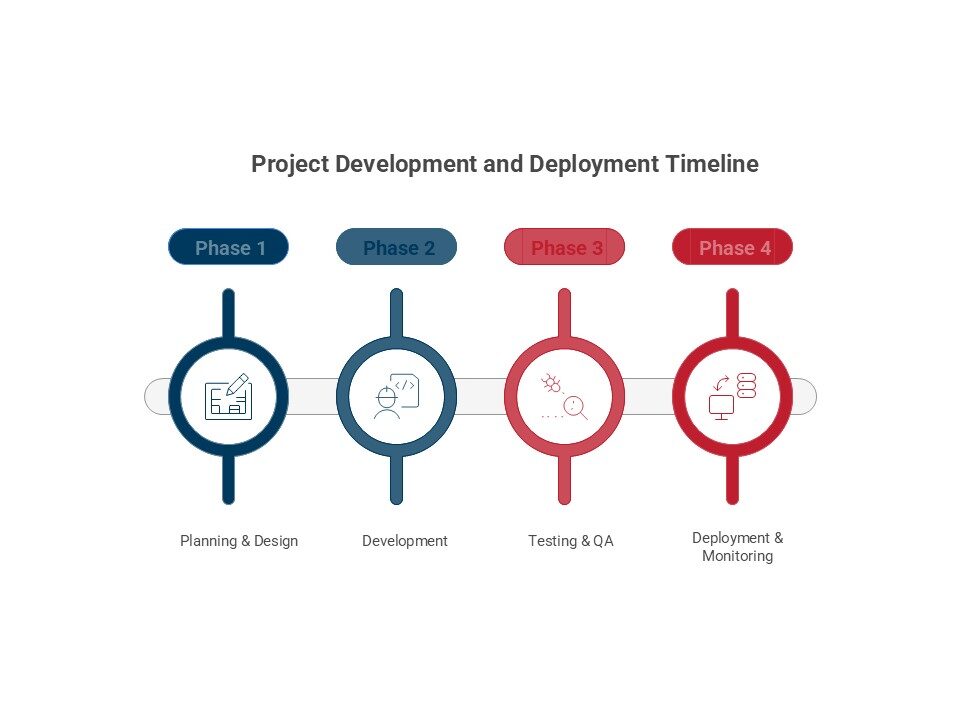
Implementation Framework: Building Your Service Delivery System
Phase 1: Assessment and Strategy Development
The journey begins with a comprehensive assessment of current service capabilities, customer expectations, and competitive positioning. This phase involves stakeholder interviews, process mapping, customer research, and gap analysis to establish baseline performance and identify improvement opportunities.
Strategic objectives should be clearly defined, including specific performance targets, timeline considerations, and resource requirements. Success metrics must be established early to guide decision-making and measure progress throughout implementation.
Phase 2: System Design and Architecture
Based on assessment findings, the next phase involves designing the optimal service delivery architecture. This includes defining service standards, creating process flows, selecting technology platforms, and establishing governance structures.
The design phase must balance ambition with practicality, ensuring that proposed solutions are both transformational and achievable within organizational constraints. Change management considerations should be integrated from the beginning to facilitate smooth implementation.
Phase 3: Technology Implementation and Integration
Technology deployment should follow a phased approach that minimizes disruption while maximizing early wins. This typically involves implementing core platforms first, followed by integration with existing systems and gradual rollout of advanced capabilities.
Training and change management are critical during this phase, as successful technology adoption depends heavily on user acceptance and capability development.
Phase 4: Process Rollout and Optimization
New processes should be rolled out systematically, with pilot programs allowing for refinement before full-scale deployment. This approach enables organizations to identify and address issues early while building confidence and momentum.
Continuous monitoring and feedback collection during rollout provide valuable insights for optimization and help ensure that theoretical designs work effectively in practice.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Organizational Resistance and Change Management
One of the most significant barriers to successful service delivery system implementation is resistance to change. This resistance can come from various sources, including concerns about job security, skepticism about new processes, or simply comfort with existing approaches.
Effective change management requires clear communication about benefits, involvement of key stakeholders in design decisions, and demonstration of early wins that build confidence in the new system. Leadership commitment and visible support are essential for overcoming resistance and maintaining momentum.
Technology Integration Complexity
Modern organizations typically have complex technology environments with multiple systems that must work together seamlessly. Integration challenges can significantly impact implementation timelines and costs if not properly managed.
Success requires careful planning, experienced technical resources, and often the involvement of specialized integration partners. Phased approaches that prioritize critical integrations while allowing for iterative improvement often prove most effective.
Maintaining Service Quality During Transition
Organizations must continue delivering excellent service to existing customers while implementing new systems and processes. This dual focus can strain resources and create operational complexity.
Effective transition management involves careful scheduling, backup procedures, and clear communication with both internal teams and external customers about any temporary impacts on service delivery.
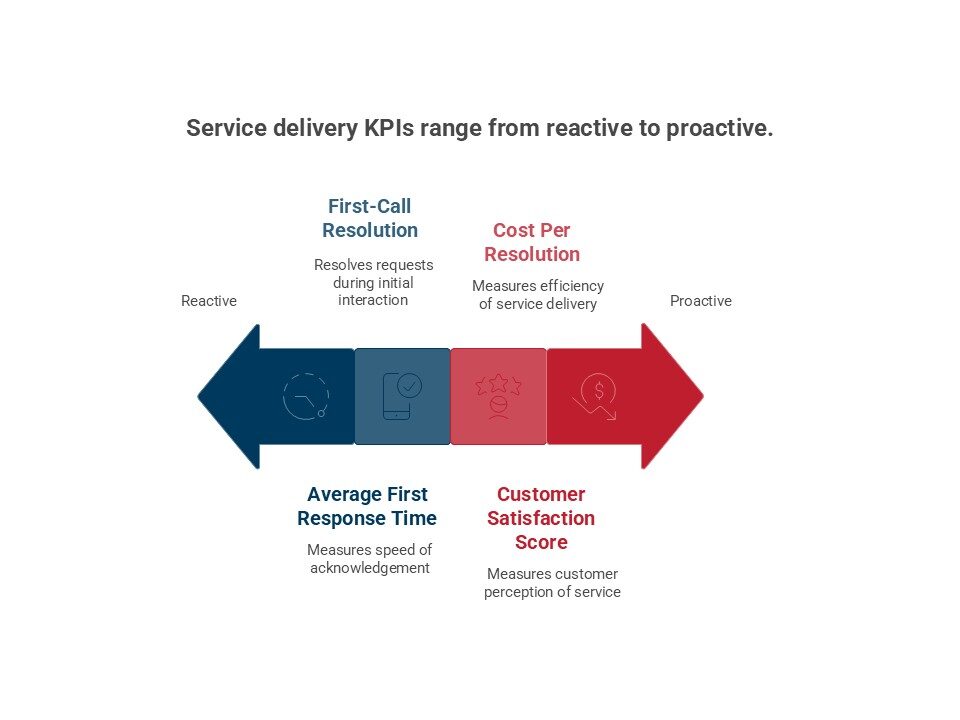
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators
Customer-Centric Metrics
The ultimate measure of service delivery system success is customer satisfaction and outcomes. Key metrics include Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores, customer effort scores, and retention rates. These metrics should be tracked continuously and segmented by customer type, service channel, and other relevant dimensions.
Operational Excellence Indicators
Internal operational metrics provide insights into system efficiency and effectiveness. These include service level achievement, response times, resolution rates, cost per transaction, and resource utilization. The goal is to optimize these metrics while maintaining or improving customer satisfaction.
Business Impact Measures
Ultimately, service delivery systems must contribute to business success. Key business metrics include revenue per customer, customer lifetime value, new customer acquisition rates, and overall profitability. The correlation between service delivery improvements and business outcomes should be clearly established and regularly monitored.
Innovation and Adaptation Metrics
In rapidly changing markets, the ability to innovate and adapt is crucial. Metrics in this category might include time-to-market for new services, employee engagement scores, and the success rate of process improvements or technology implementations.
The Future of Service Delivery Systems
Artificial Intelligence and Automation
AI and machine learning are transforming service delivery by enabling predictive analytics, intelligent automation, and personalized customer experiences. Recent McKinsey research indicates that 47% of organizations have experienced at least one consequence from AI implementation, highlighting both the opportunities and challenges associated with these technologies.
Future service delivery systems will increasingly leverage AI for tasks such as demand forecasting, resource optimization, and proactive issue resolution. However, the human element remains crucial for complex problem-solving and relationship building.
Omnichannel Integration
Customers expect seamless experiences across all channels, from digital self-service to human-assisted support. Future service delivery systems will provide truly integrated omnichannel experiences where customer context and preferences are maintained regardless of interaction channel.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Organizations are increasingly expected to demonstrate environmental and social responsibility in their operations. Service delivery systems must incorporate sustainability considerations while maintaining efficiency and effectiveness.
Getting Started: Your Service Delivery Transformation Journey
Implementing a comprehensive service delivery system requires significant commitment and resources, but the benefits justify the investment. Organizations should begin with a clear assessment of their current capabilities and a realistic understanding of their transformation goals.
Consider starting with a focused pilot program that addresses a specific service area or customer segment. This approach allows for learning and refinement while demonstrating value to stakeholders and building organizational confidence.
Success depends on strong leadership commitment, adequate resource allocation, and a willingness to adapt based on learning and feedback. Organizations that approach service delivery transformation systematically and strategically position themselves for sustained competitive advantage in an increasingly service-centric economy.
Additional Resources
For deeper insights into service delivery system design and implementation:
- HubSpot’s Customer Service Statistics 2024 – Comprehensive data on customer service trends and performance benchmarks
- McKinsey Digital on Business Value of Design – Strategic insights on design-driven business transformation
- Service Delivery Platform Market Analysis – Industry growth trends and market dynamics
- McKinsey Technology Trends 2024 – Technology trends impacting service delivery
- Business Operations in 2024 – Operational excellence insights for the modern era
Ready to transform your service delivery? Contact our team to discuss how a systematic approach to service delivery can drive growth and operational excellence for your organization.
Main: (240) 242-5650
Cell: (301) 661-4018